
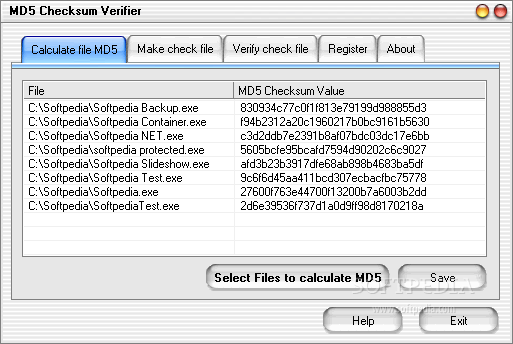
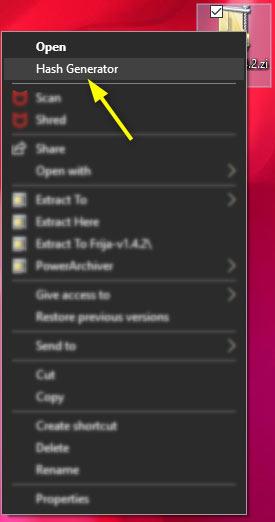
On Windows 10 (and probably previous versions) follow these steps: This is how I calculate checksums from Explorer using no third-party software. Optional: check - the signature you want to check. Hash algorithms: MD2 MD4 MD5 SHA1 SHA256 SHA384 SHA512Ĭhecksum filepath Get-FileHash Ĭ:\>certutil -hashfile -v /? | findstr goriĬertUtil -hashfile InFile You can quickly check the available options like this: C:\>powershell -c "Get-FileHash -?" | findstr gori So specify your algorithm explicitly where needed. Note that the powershell Get-FileHash default is SHA256, while certutil still defaults to SHA1. I included an extra space character for backward-compatibility with older certutil versions, but it is optional. Why is that actual anti-hex regex so weird ? See this question to learn how regex ranges in findstr don't work as they should.
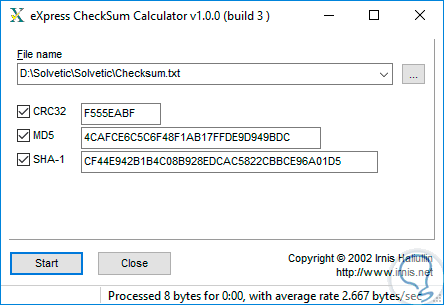
C:\>CertUtil -hashfile "C:\windows\fonts\arial.ttf" | findstr -vrc:"" That should also make it safer for other locales and languages. To make this more resilient against breakage from yet another future change in certutil, we should look for lines with non-hex characters to filter out. The extraneous spaces are gone too - one less thing to worry about when scripting. The certutil output seems to have changed since Windows 8, so my old filter to isolate the hash doesn't work anymore. I am adding this here only because I didn't see any fully working powershell examples, ready for copy-paste: C:\> powershell "Get-FileHash %systemroot%\system32\csrss.exe"


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
